How Did Imperialism Affect The World?
Imperialism, a period where powerful empires in Europe extended their influence over others for economic, political, and cultural gain. But how exactly did imperialism affect the world?
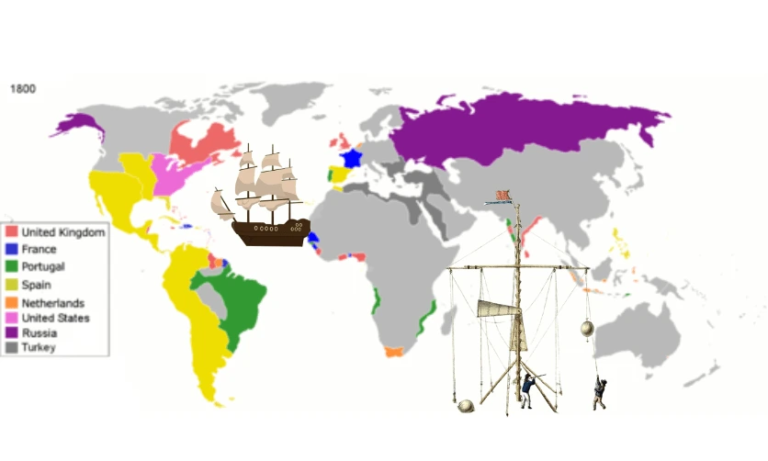
The Rise of Imperialism
Imperialism began in the 15th century but reached its zenith between the 19th and early 20th centuries. Before this era, nations like China practiced imperialism as a means of extending their power. However, it was European nations such as Britain, France, Germany, and Belgium that aggressively expanded their empires through maritime exploration. By colonizing large parts of Asia, Africa, and the Americas, these empires gained political and economic advantages by extracting raw materials, accessing new trade markets, and utilizing cheap labor.
Economic Impacts
One of the most significant effects of imperialism was economic transformation. Some aspects of it include:
- The colonies produced commodities like cotton, rubber, tea, and minerals, which were shipped back to the mother countries. These raw materials fueled industrial growth and substantially improved the lifestyle of Europeans. In contrast, the colonies often suffered under this arrangement. Frequently, the commodities produced were neither consumable locally nor permissible for trade outside the empire, leading to widespread poverty and starvation. Today, many of these former colonies, now independent nations, still produce these commodities, which in some instances form a substantial part of their export economy.
- The complex trade network established during imperialism to connect various parts of the world has immensely shaped modern-day trade. Moreover, the trade policies and legal frameworks developed during this period have laid the groundwork for the systems governing international trade today.
- The 16th and 17th-century joint-stock companies, which emerged during the era of European exploration and colonization, played a pivotal role in funding large state ventures associated with imperialism. Some examples of early joint-stock companies include the British East India Company, the Dutch East India Company, and the Virginia Company. Their influence continues to impact modern companies, particularly in terms of capital raising, risk management, and the pursuit of ambitious commercial endeavors.
Political and Social Changes
The introduction of western legal systems and governance policies favorable for the empires was the key to maintaining political control over their colonies. For instance, British common law was introduced in colonies like India, Australia, and parts of Africa, while French civil law influenced legal systems in parts of Africa and Southeast Asia.
Customary Laws and Dual Legal Systems
In some colonies, the imperial powers allowed the continuation of local, customary laws for personal matters like marriage, while imposing Western laws for criminal and commercial cases. This led to the creation of dual legal systems which persist in many countries.
Human rights and International Law
The negative experiences and atrocities that these colonies faced set the stepping stone for the creation of human rights and international law. Many principles of current international law, such as self-determination and anti-discrimination, can be traced back to the anti-imperialist movements.
Imperialism’s impact was multifaceted: it facilitated the spread of new ideas, languages, and technologies, but also often suppressed local cultures and traditions. Education systems were redesigned to promote the colonizer’s language and values, profoundly affecting the identity and heritage of the colonized peoples.
Science and Technology
With abundant resources and forced labor, Europeans had more time for scientific and technological advancement. This fostered the development of industries and processes, further enhancing their ability to expand and colonize, as navigation, weaponry, communication, and tools became more sophisticated. Some crucial advances included:
- Telegraph – Before telegraphs, it would take about 2 years for a message to go and come back between Europe and India. Telegraphs made it possible to deliver and receive messages instantaneously, which vastly improved the efficiency of governing colonies from within Europe.
- Discoveries in medicine – Quinine, derived from the bark of the cinchona tree, was discovered in the 17th century as a treatment for malaria, a common disease among European settlers in the colonies in Africa. This discovery saved countless lives and remains an important tool in the fight against malaria today. In the late 19th century, Louis Pasteur’s work on bacteriology led to the discovery of vaccines and treatments for diseases such as anthrax, rabies, and cholera. This has had a lasting impact on modern medicine, with vaccines and treatments continuing to be developed based on Pasteur’s principles. Overall, the encounters between Europeans and indigenous populations during the era of imperialism led to significant advancements in medicine, including the discovery of quinine and the work of Pasteur on bacteriology, which have had a lasting impact on public health.
Resistance and Nationalism
Imperialism was not accepted passively. It faced resistance from local populations. This resistance sometimes took the form of armed rebellion, while in other cases, it manifested as political movements seeking self-determination. This struggle against imperial powers ignited a sense of nationalism in many colonized countries, laying the groundwork for future independence movements.
World War I and the End of Imperialism
At the beginning of the 20th century, several nations aspired to assert themselves as dominant global powers. Notable among these were Russia, Germany, and Japan. This ambitious expansionism heightened tensions across European empires, leading to a complex web of alliances that ultimately escalated into World War I.
Conclusion
In summary, imperialism was a powerful force that reshaped the world in myriad ways. Its impact was profound, with economic, political, social, and cultural ramifications that continue to be felt today. Understanding the complexities of imperialism helps us comprehend the current global landscape and the historical roots of many modern issues. As we reflect on this period, it’s essential to recognize both the advancements it brought and the challenges it created, shaping a more nuanced view of our shared history.
